Abstract
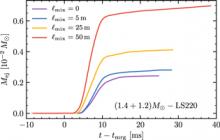
General-relativistic simulations of binary neutron star (NS) mergers with viscosity reveal a new outflow mechanism operating in unequal mass binaries on dynamical timescales and enabled by turbulent viscosity. These "viscous-dynamical" ejecta are launched during the merger due to the thermalization of mass exchange streams between the secondary and the primary NS. They are characterized by asymptotic velocities extending up to ~0.8c, and have masses that depend on the efficiency of the viscous mechanism. Depending on the unknown strength of the effective viscosity arising from magnetohydrodynamic instabilities operating during the merger, the overall mass of the dynamical ejecta could be enhanced by a factor of a few and the mass of the fast tail of the ejecta, having asymptotic velocities ≥0.6c, by up to four orders of magnitude. The radioactive decay of the expanding viscous-dynamical ejecta could produce bright kilonova transients with signatures of free neutron decay in the first hour, and enhanced near-infrared flux on a timescale of a few days. The synchrotron remnant produced by the interaction between the ejecta and the interstellar medium could also be significantly enhanced by viscosity. Such a remnant could be detected in the case of GW170817 as a rebrightening of the radio signal in the next months to years.