Abstract
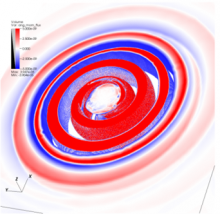
The AT2017gfo kilonova (kN) counterpart of the binary neutron star merger event GW170817 was characterized by an early-time bright peak in optical and UV bands. Such blue kN is commonly interpreted as a signature of weak r-process nucleosynthesis in a fast expanding wind whose origin is currently debated. Numerical relativity simulations with microphysical equations of state, approximate neutrino transport, and turbulent viscosity reveal a new hydrodynamics-driven mechanism that can power the blue kN. Spiral density waves in the remnant generate a characteristic wind of mass ~10−2  and velocity ~0.2 c. The ejected material has an electron fraction mostly distributed above 0.25 being partially reprocessed by hydrodynamic shocks in the expanding arms. The combination of dynamical ejecta and spiral-wave wind can account for solar system abundances of r-process elements and early-time observed light curves.
and velocity ~0.2 c. The ejected material has an electron fraction mostly distributed above 0.25 being partially reprocessed by hydrodynamic shocks in the expanding arms. The combination of dynamical ejecta and spiral-wave wind can account for solar system abundances of r-process elements and early-time observed light curves.